CIAJ conducted its annual study of mobile device use and announces the release of this year’s findings as follows.
MVNO awareness and market penetration have grown over the past year, with the ratio of people who have actually used MVNOs increasing. According to a study of monthly payments, cheaper plans are gaining popularity among subscribers, which can be assumed to be a direct impact of MVNOs. “Price” was also ranked among the top responses when asked about what factors would be important on their next purchase. All of this leads to the conclusion that demand for low prices is mounting among users.
(1) Summary
This study has been conducted as a fixed-point observation every April since 1998 to capture on-going changes in the domestic mobile communications market and include data from the busiest sales season of the year in March.
CIAJ mailed questionnaires to 1,200 mobile phones users (100 male & 100 female users in each of the following age groups: under twenty, twenties, thirties, forties, fifties, sixties) residing in the larger Tokyo and Osaka metropolitan areas from the end of March through early April of this year.
Unique findings from this year’s study are as follows.
(2) Handset Trends
<Type of terminal owned>
- The 1,200 people surveyed owned a total of 1,726 terminals and their breakdown is listed in the following table.
- 1,088 respondents (90.7%) said their main-use terminal (primary choice terminal) was a smartphone, while 110 respondents (9.2%) said it was a feature phone.
<Type of terminal owned by respondents of study>
Type of terminal owned No. of devices Main-use device
(Primary choice)Smartphone 1,090 (90.8%) 1,088 (90.7%) Featurephone 123 (10.3%) 110 (9.2%) Tablet (with telecom subscription) 232 (19.3%) 1 (0.1%) Tablet (with only Wi-Fi connectivity) 80 (6.7%) 1 (0.1%) Mobile Wi-Fi router 197 (16.4%) 0 PHS 4 (0.3%) 0 Total (including other responses) 1,726 1,200 (100.0%)
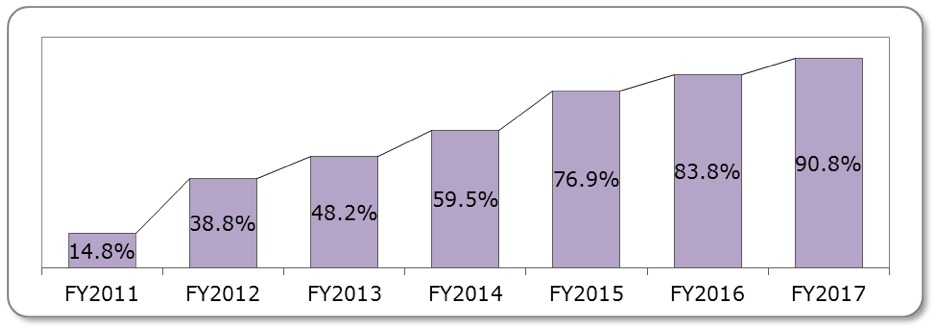
<Accelerated growth in smartphone users continues>
- The 2017 survey showed continuous growth in smartphone users with a 7.0% increase to 90.8%.
- Smartphone use among respondents in their teens, twenties and thirties had nearly reached 100% in last year’s study, but the 2017 study reveals that penetration has spread in older generations, with respondents in their fifties exceeding 80% and exceeding 60% among those in their sixties.
<Change in Percentage of Smartphone Users Over the Years>
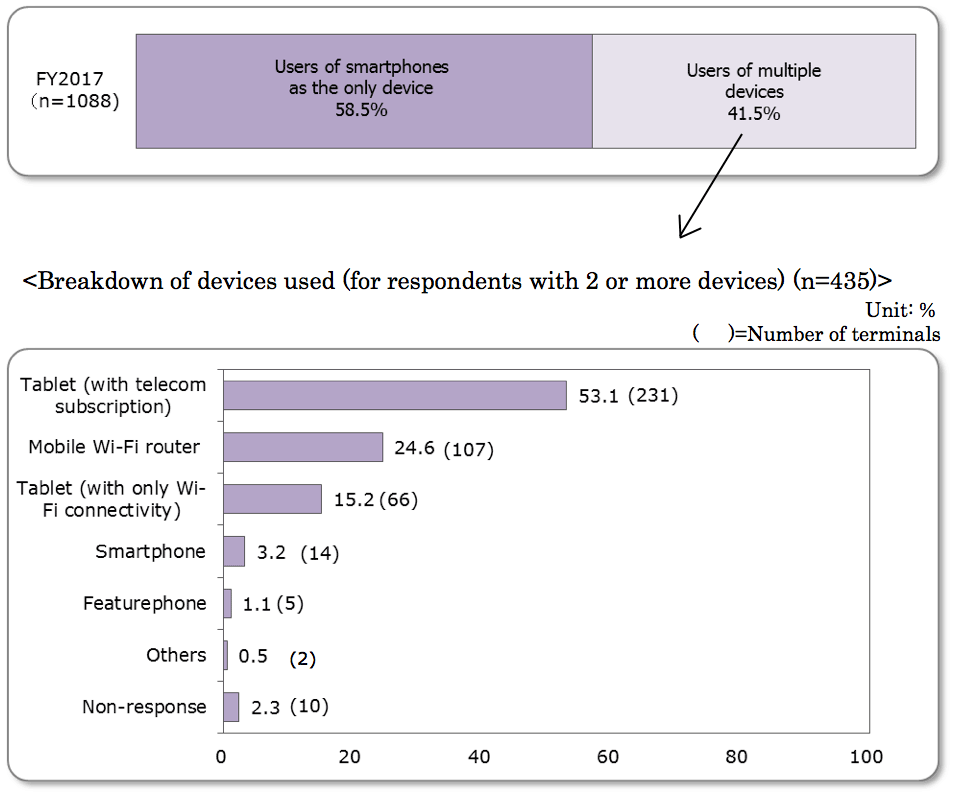
<Tablets are dominant as second device, but flat growth>
- Of the 1,088 smartphone users, 435 (41.5%) were using multiple devices, an increase of 5.6 points (last year’s multi-device users were 351 (35.9%)) over the previous year.
- The rate of respondents who use tablets (with telecom subscription) was still the most popular choice as a second device, but the total number of devices for tablets with both telecom subscription and only wi-fi connectivity decreased slightly from 304 in 2016 to 297 and so did the ratio of users.
- On the other hand, the number of respondents using mobile wifi routers increased from 9.4% to 24.6%.
(3) Trends ion New Services
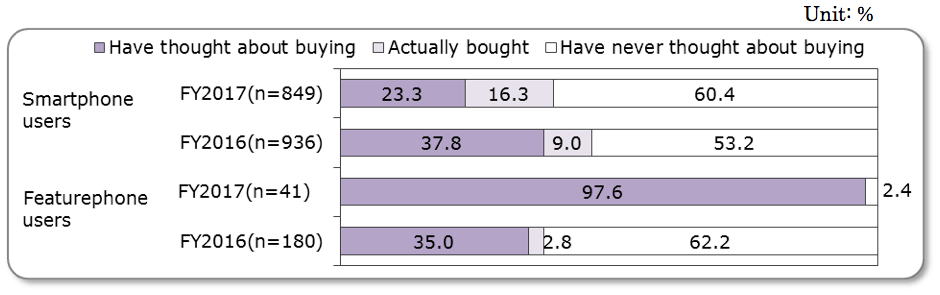
<MVNO ultra low-end smartphone users still a minority but expected to grow>
- 79.6% of smartphone users (n=1,067) stated that they were aware of MVNO.
- Of smartphone users, 16.3% had actually bought an ultra low-end smartphone, compared to 9.0% in the 2016 survey, reflecting their penetration in the market.
<MVNO Ultra Low-End Smartphone Use>
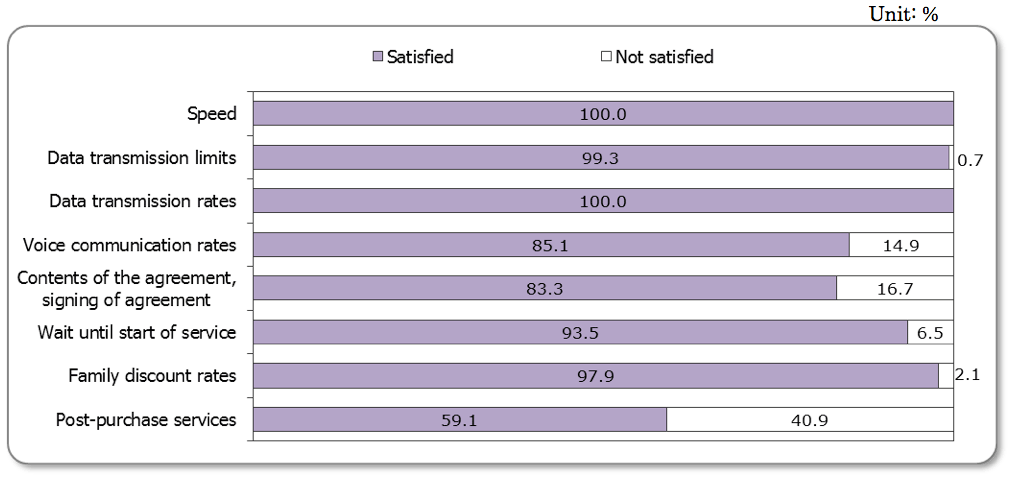
<Satisfaction with MVNO>
- MVNO users (n=138) gave high marks about the service, with high satisfaction concerning speed, data transmission limits, rates and other items. The number of those surveyed who were happy with the family discount rates jumped from 57.0% to 97.9%. However, satisfaction rates for post-purchase services dropped from 91.9% to 59.1%.
<Views After Trying MVNO>
(4) Purchasing Cycles
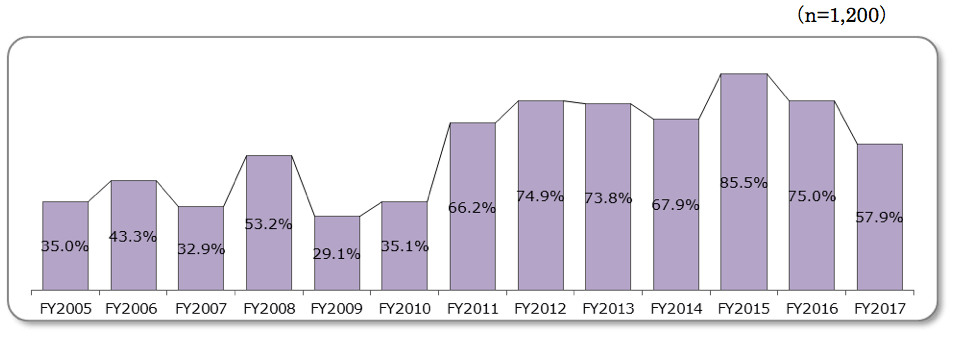
<Slowing growth in intention to replace devices>
- 57.9% of respondents indicated intention to purchase a replacement, showing a continuation of a downward trend. This drop was especially prevalent among smartphone users, dropping from last year’s 85.1% to 60.5%.
<Intent to purchase replacement of current model>
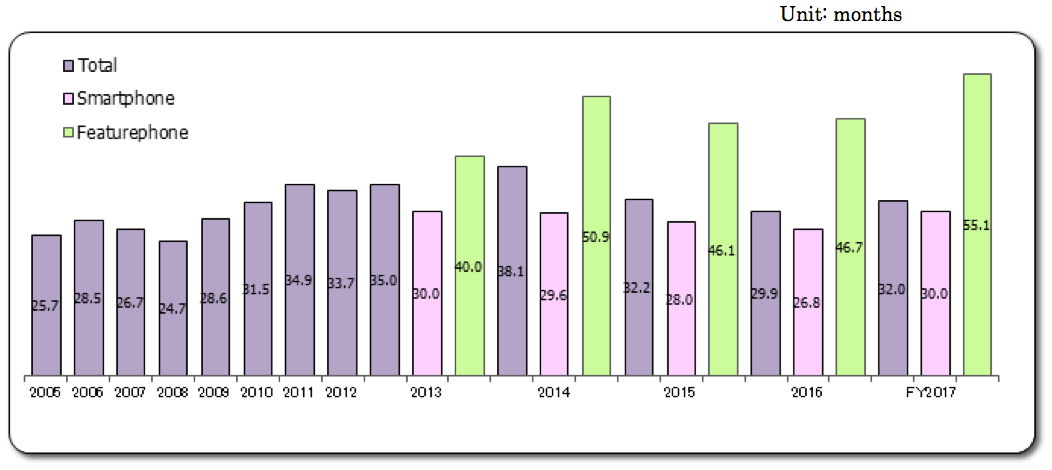
<Longer purchasing cycles>
- The average use of respondents’ previous model (the one before the handset currently in use) was 30.0 months for smartphones and 55.1 months for featurephones and 32.0 overall. The cycle for smartphones had been shortening until last year, but converted to longer duration this year, indicating a lull in the purchase of smartphones.
<Change in Duration of Ownership>
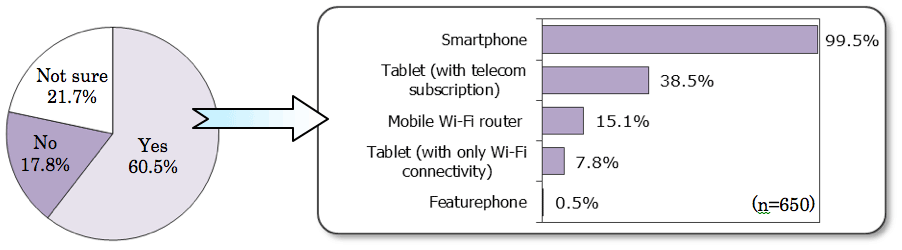
<Next purchase likely to be a smartphone again>
- Among smartphone users, 99.5% of those intending to purchase a replacement responded that they planned to choose a smartphone again.
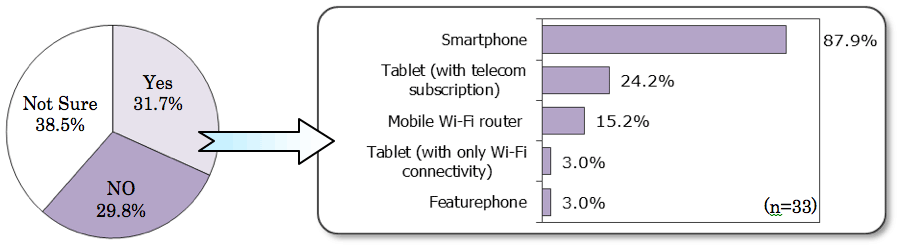
- Among featurephone users, 87.9% of those intending to purchase a replacement responded that they planned to choose a smartphone, leading to the conclusion that smartphone user rates will continue to grow.
<Intent to purchase replacement of current smartphone (n=1,079)>
<Intent to purchase replacement of current featurephone (n=104)>
(5) Decisive Factors for New Purchases
<Decisive factors in purchasing smartphones/feature phones>
- The top ranking decisive factors in making the next purchase for smartphone users were “purchase price of handset,” “monthly payment cost,” “design” and “size (snugness in one’s hand),” with all items exceeding 80% and last year’s top choice, “manufacturer/brand.” The top two factors, “purchase price of handset” and “monthly payment cost,” jumped from 3rd and 4th place in 2016, reflecting user emphasis on cost.
- Top ranking factors for featurephone users were also “purchase price of handset” and “monthly payment cost.”
<Decisive factors in purchasing smartphones/featurephones>
| Rank | Smartphones (n=1,077) | % |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Purchase price of handset | 87.7 |
| 2 | Monthly payment cost | 87.6 |
| 3 | Design | 82.0 |
| 4 | Size (snugness in one’s hand) | 80.8 |
| 5 | Manufacturer/brand | 75.0 |
| 6 | Size (lightweight) | 72.9 |
| 7 | Water-proof | 70.5 |
| 8 | Battery life | 65.9 |
| 9 | Mobile telecom operator | 57.1 |
| 10 | Camera (video, still photos) | 55.0 |
| 11 | Color | 52.6 |
| 12 | High-speed service | 51.3 |
| 13 | Size of LCD | 48.7 |
| 14 | Operability (reaction speed, ease of use) | 44.9 |
| 15 | CPU capacity | 44.2 |
| 16 | Beautiful display | 39.9 |
| 17 | On-board memory capacity | 37.0 |
| 18 | Music player features | 31.8 |
| 19 | Maximum capacity of external memory | 25.2 |
| 20 | Wireless charging system | 24.1 |
| 21 | Pixel count of displayfiles | 22.8 |
| 22 | Dust resistancy | 19.3 |
| 23 | Existing security features of the device | 15.7 |
| 24 | Able to continue using mobile operator services | 15.6 |
| 25 | Ability to read PC files | 14.9 |
| 26 | Durability (toughness) | 13.6 |
| 27 | Handwriting and hand drawing recognition | 12.5 |
| Rank | Featurephones (n=104) | % |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Purchase price of handset | 80.8 |
| 2 | Monthly payment cost | 78.8 |
| 3 | Size (snugness in one’s hand) | 45.2 |
| 4 | Design | 41.3 |
| 5 | Size (lightweight) | 40.4 |
| 6 | Water-proof | 34.6 |
| 7 | Battery life | 26.0 |
| 8 | Size of LCD | 26.0 |
| 9 | Mobile telecom operator | 20.2 |
| 10 | Manufacturer/brand | 19.2 |
| 11 | Color | 15.4 |
| 12 | Camera (video, still photos) | 13.5 |
| 13 | Beautiful display | 11.5 |
| 14 | Dust resistancy | 10.6 |
| Operability (reaction speed, ease of use) | ||
| Ability to watch tv broadcast | ||
| 18 | On-board memory capacity | 9.6 |
| 19 | High-speed service | 8.7 |
| 20 | Same operability as previous phone | 7.7 |
| 21 | Pixel count of displayfiles | 6.7 |
| 22 | Music player features | 5.8 |
| 23 | Infrared communication features | 5.8 |
(6) Use of Handset Features and Services
<Changes in use of smartphone features and services>
- The study has looked at the use of various features and services of mobile handsets over the years. The table below indicates user ratio and year-over-year change in use, duration and frequency.
- The use of features and services are diverse and it is the hope of this committee that manufacturers reflect these trends in future designs of their products and services.
<Change in Use of Smartphone Features and Services>
Use scenario Rate of use (%) Duration and
frequency of use2016 2017 Voice communication (circuit switched) 97.1 → 96.3 ↗ IP phone (LINE, Skype, etc.) 56.4 ↘ 19.6 ↘ SMS/MMS 88.2 → 87.7 ↗ Carrier mail 8.1 ↗ 12.7 → Internet mail 86.7 ↘ 81.9 ↗ SNS messages 91.7 → 92.1 → Normal e-mail based on text 93.6 → 91.8 ↗ Decorated messages, emoji 64.8 ↘ 51.2 ↗ Photo-attached e-mail 84.2 ↘ 63.6 ↘ Video-attached e-mail 48.2 ↘ 30.1 ↘ Downloading music 80.3 ↘ 67.8 ↗ Downloading video 73.2 ↘ 64.9 ↗ Downloading games 78.0 → 75.0 ↗ Downloading items for games 43.9 → 46.6 ↗ Downloading digital books 40.1 ↘ 29.8 ↗ Downloading stamps 45.4 ↗ 57.9 ↗ Viewing and writing in LINE 93.3 → 91.7 → Watching videos 85.0 → 84.9 ↗ Music features 83.8 ↘ 66.7 ↘ Viewing and writing inTwitter, Facebook and other SNS 84.7 ↘ 80.0 ↗ Watching news and reading newspapers 48.3 ↗ 56.1 ↗ Watching tv 10.1 ↗ 38.6 ↗ Internet payments 77.6 ↘ 43.3 → Using camera for still photos 91.6 ↘ 87.6 ↘ Using camera for video 53.9 ↗ 58.7 ↘ Maps, navigation, GPS logger, location information 86.9 ↘ 73.9 → Scheduling 82.0 ↘ 67.2 → Cloud memo management 44.8 ↘ 28.8 ↘ Viewing PC files (Office, PDF, etc.) 38.0 ↘ 25.1 ↘ Using coupons 70.7 ↘ 62.5 ↘ Text entry using voice recognition 48.8 ↘ 25.1 ↘ QR code 66.0 ↘ 62.1 ↘ Translation apps using voice recognition 48.0 ↘ 22.6 ↘ Bluetooth (wireless headsets, keyboards, etc.) 47.6 ↘ 13.2 ↘ International roaming, use abroad 27.0 ↘ 17.4 ↗
Arrows under rate of use as well as duration and frequency of use indicate change over the previous year.
For details, contact
Products & Technologies Development
CIAJ
tel: 81-3-5403-9358 fax: 81-3-5403-9360
For more general inquiries, contact
Corporate Communications
CIAJ
tel: 81-3-5403-9351 fax: 81-3-5403-9360